thank you for visiting the labor history resource project as we build this resource!
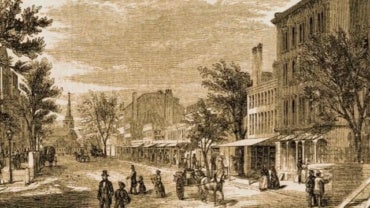
The film describes the extraordinary anti-slavery efforts taking place in the mid-19th century in Lowell. Forrant and Grooms visit the sites that still exist in downtown Lowell where abolitionist activity occurred and where freedom seekers operated businesses.

The Lowell mill girls were young female workers who came to work in industrial corporations in Lowell, Massachusetts, during the Industrial Revolution in the United States.

In the early 19th century the United States of America began to experience many changes. In parts of the country there was a shift from an agrarian society to an industrial society.

In the early 19th century the United States of America began to experience many changes. In parts of the country there was a shift from an agrarian society to an industrial society.

Lowell built on the advances made in the British textile industry, such as the use of the power loom, to industrialize American textile production. He was the first factory owner in the United States to create a textile mill that was vertically integrated.
The Boott Cotton Mills Museum gives a snapshot of what is was like to work in New England cotton mills in the 1800s. The Museum, once Boott Mill #6, was originally owned by Kirk Boott, an industrialist who was responsible for much of the early urban planning that shaped Lowell’s industrial and residential landscape.

In 1820 Lowell, known as East Chelmsford, MA at the time, had a population of 200 and was a farming community. Thirty years later, the population had grown to 33,000 and one could find 32 textile mills in existence there. Lowell was an ideal location for these mills because it was located near the Merrimac River. The river supplied the water necessary to run these factories.

