As early as the 1830s, many U.S. states had enacted laws restricting or prohibiting the employment of young children in industrial settings. However, in rural communities where child labor on the farm was common, employment of children in mills and factories did not arouse much concern. Another problem for children was the popular opinion that gainful employment of children of the “lower orders” actually benefited poor families and the community at large.
About Lewis Hine
Photographer Lewis W. Hine (1874-1940) was born in Oshkosh, Wisconsin. He studied sociology at Chicago and New York universities, becoming a teacher, then took up photography as a means of expressing his social concerns.
His first photo essay featured Ellis Island immigrants. In 1908, Hine left his teaching position for a full-time job as an investigative photographer for the National Child Labor Committee, which was then conducting a major campaign against the exploitation of American children.
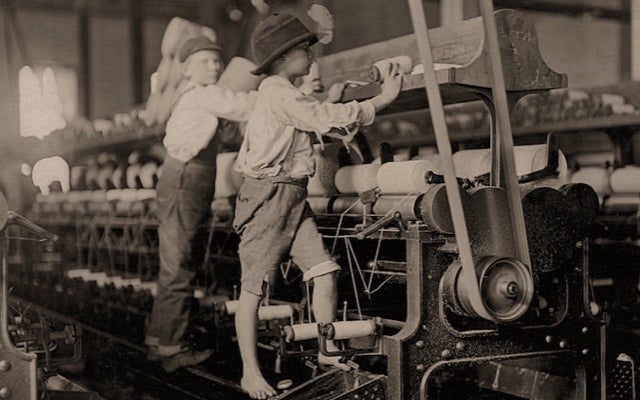
From 1908 to 1912, Hine took his camera across America to photograph children as young as three years old working for long hours, often under dangerous conditions, in factories, mines, and fields. Hine was an immensely talented photographer who viewed his young subjects with the eye of a humanitarian.
In 1909, he published the first of many photo essays depicting working children at risk. In these photographs, the essence of wasted youth is apparent in the sorrowful and even angry faces of his subjects. Some of his images, such as the young girl in the mill glimpsing out the window, are among the most famous photographs ever taken.
During World War I, he documented the plight of refugees for the American Red Cross. He later documented the construction of the Empire State building in 1930-1931 and even hung upside down from a crane to photograph workmen.